Conditional Statements - Jupyter Notebook
Instructions
1. Complete the code in the editor to find the average rating for free apps.
3. Modify the existing code in the editor on the right to compute the average rating of non-free apps.
Optional exercise: Inspect the value of avg_rating_non_free and compare the average with that of free apps (the average rating of free apps is approximately 3.38 — we computed it in the first screen). Can we use the average values to say that free apps are better than non-free apps, or vice versa?
4. Following the same techniques we used in the diagram above, compute the average rating of non-gaming apps.
Optional exercise: Compare the average rating of gaming apps (3.69) with that of non-gaming apps. Why do you think we see this difference?
5. Complete the code in the editor to compute the average rating of free gaming apps.
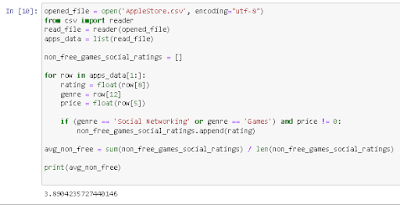
6. Complete the code in the editor to compute the average rating of the apps whose genre is either "Social Networking" or "Games."
7. Compute the average rating of non-free apps whose genre is either "Social Networking" or "Games."
8. Compute the average rating of the apps that have a price greater than 9.
Find out how many apps have a price less than or equal to 9 and assign the result to a variable named n_apps_less_9. The list of ratings from the first question can help you find a quick answer.
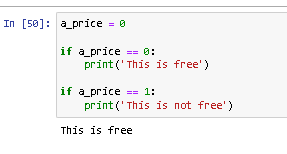
9. Complete the code in the editor to label each app as "free" or "non-free" depending on its price.
10. Complete the code in the editor to label each app as "free," "affordable," "expensive," or "very expensive." Inside the loop:
Inspect the header row and the first five rows to see some of the changes you made.
THANK YOU !!
 Reviewed by bella sevenia
on
Oktober 17, 2023
Rating: 5
Reviewed by bella sevenia
on
Oktober 17, 2023
Rating: 5